Introduction
I have been spending some time working with the latest Apose.Email for .NET. It has been twelve or thirteen years since I have written any email related code. Back in the early 2000s, I did a little bit of work with Visual Basic and the Outlook Collaboration Data Objects (CDO). We have come a long way since that time. Email in the cloud is now becoming the norm with Gmail and Office 365.
There’s still plenty of need for local and Exchange based email processing in business applications as well. I will get to one possible scenario in my own application below.
Latest Aspose.Email Release
The Aspose.Email library supports just about any email related activity imaginable. Here is just a handful of scenarios developers can code into their own applications with Aspose.Email:
Generate emails and send via SMTP
- Embed objects in message body – Send emails with embedded images or documents.
Attach files – Attach files to an email as a user would from their email client.
Mail merge – Powerful support for mail merge and mass emailing.
iCalendar support – Read and manipulate calendar events via the iCalendar standard.
Receive POP3 mail
- Work with IMAP mail sources
- Authentication
- Work with messages and folders
- SSL support (for POP3 and SMTP)
Message Files
- EML/MSG/MHT formats – All common mail message formats are supported.
- Work with files or streams – Open messages from disk or network streams.
- Manipulate PST files – Create, read and manipulate Outlook PST files and their contents.
MS Exchange Server
- WebDav and Exchange Web Services support
- Unified Messaging operations
- Send emails and Meeting Invites
Advanced support for recurrence
- Easily and reliably calculate event recurrence
- Suppoprt for iCalendar (RFC 2445)
Detailed developer documentation for all of the Aspose.Email features is available online here.
So, whether your application needs to work with Exchange, Outlook files, POP3/SMTP, or talk to Gmail via IMAP, Aspose.Email has APIs to help with each situation. There are also sample apps for each feature exposed in Aspose.Email to get developers started off on the right track.
An IMAP Console Application
There are dozens of sample applications installed along with Apose.Email. To get started, launch the Aspose Examples Dashboard:
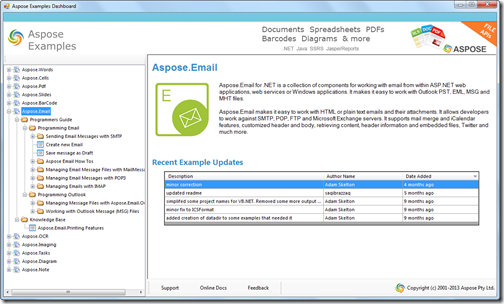
The example apps are grouped by feature set. Developers can view the code in the Sample Browser, launch the solution in C# or VB, or run the example app right from the Browser application.
I decided to take a closer look at one of the IMAP samples. The one I chose was “Fetch Messages from IMAP Server and Save to Disk”, which does exacly what the name implies. It is a console application that connects to a Gmail account via IMAP, selects the Inbox folder and loops through all of the messages, saving each one to a local folder in the “.eml” format. Here is the complete code implementation for the app after a couple of ReSharper refactorings.
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// The path to the documents directory.
string dataDir = Path.GetFullPath("../../../Data/");
Directory.CreateDirectory(dataDir);
//Create an instance of the ImapClient class
var client = new ImapClient
{
Host = "imap.gmail.com",
Username = "asposetest123@gmail.com",
Password = "F123456f",
Port = 993,
SecurityMode = ImapSslSecurityMode.Implicit,
EnableSsl = true
};
try
{
client.Connect();
//Log in to the remote server.
client.Login();
// Select the inbox folder
client.SelectFolder(ImapFolderInfo.InBox);
// Get the message info collection
ImapMessageInfoCollection list = client.ListMessages();
// Download each message
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
{
//Save the EML file locally
client.SaveMessage(list[i].UniqueId, dataDir + list[i].UniqueId + ".eml");
}
//Disconnect to the remote IMAP server
client.Disconnect();
System.Console.WriteLine("Disconnected from the IMAP server");
}
catch (System.Exception ex)
{
System.Console.Write(ex.ToString());
}
}
It is simple and intuitive to use.
The PST Archive Utility
I didn’t have the time to write my own applications that use every aspect of the library, so I decided to take one set of features and focus there. For years, I have been meaning to organize my work-related PST files into yearly archives. In fact, I have one PST that covers nearly seven years of email. It is nearly 6gb in size and contains who knows how many thousands of items.
I built a small utility that will read a selected PST file, iterate through all of its folders and move all items for the specified year into a new PST with the year prepended to the PST’s file name, mirroring the folder structure of the original PST. I decided to build the utility as a WPF application, but this could function nicely as a command line utility also.
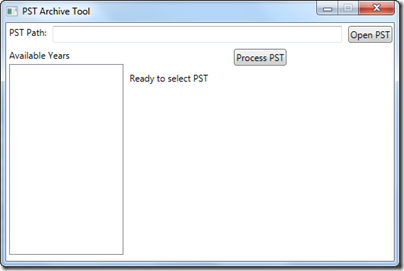
Using the utility is rather straightforward, simply:
- Enter the full path to the PST to be read.
- Click ‘Open PST’.
- The available years will display. Select a year.
- Click ‘Process PST’.
- When complete, the status message will update to “New PST Created for Year xxxx”.
The code to display the available years iterates through the folders and items, collecting the unique years into a List<int>. It then sorts them before setting the property in the ViewModel to which the Available Years ListBox is bound.
/// <summary>
/// Gets all the years of items in a PST file.
/// </summary>
private void GetPstYears()
{
if (String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(PstPath) || !File.Exists(PstPath)) return;
using (PersonalStorage mainPst = PersonalStorage.FromFile(PstPath, true))
{
CurrentStatus = "Processing Years...";
List<int> years = GetAvailableYears(mainPst.RootFolder);
years.Sort();
Years.Clear();
foreach (int year in years)
{
Years.Add(year);
}
CurrentStatus = "PST Ready";
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the available years in a specified Outlook folder.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="folder">The folder.</param>
/// <returns>A list of years.</returns>
private List<int> GetAvailableYears(FolderInfo folder)
{
var years = new List<int>();
foreach (MapiMessage message in
folder.EnumerateMapiMessages().Where(message => !years.Contains(message.DeliveryTime.Year)))
{
years.Add(message.DeliveryTime.Year);
}
foreach (int subYear in from folderInfo in folder.EnumerateFolders()
where folderInfo.HasSubFolders
select GetAvailableYears(folderInfo)
into subYears
from subYear in subYears
where !years.Contains(subYear)
select subYear)
{
years.Add(subYear);
}
return years;
}
Similarly, the code to move the messages for the selected year to the new PST, iterates the folder structure to find any matching items.
/// <summary>
/// Process a PST by moving items from a selected year to a new PST
/// while creating the same folder structure.
/// </summary>
private void ProcessPst()
{
if (SelectedYearIndex < 0 || String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(PstPath) || !File.Exists(PstPath)) return;
int year = Years[SelectedYearIndex];
using (PersonalStorage mainPst = PersonalStorage.FromFile(PstPath, true))
{
string newFileName = PstPath.Insert(PstPath.LastIndexOf("\\", StringComparison.Ordinal) + 1, year.ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
using (PersonalStorage pstWithYear = PersonalStorage.Create(newFileName, FileFormatVersion.Unicode))
{
ProcessSubfolders(mainPst.RootFolder, pstWithYear.RootFolder, year);
}
}
CurrentStatus = String.Format("New PST Created for Year {0}", Years[SelectedYearIndex]);
}
/// <summary>
/// Processes the subfolders of a provided PST folder and adds items
/// from the specified year to the new folder provided.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="folder">The source folder.</param>
/// <param name="newParentFolder">The new folder.</param>
/// <param name="year">The year of items to move.</param>
private void ProcessSubfolders(FolderInfo folder, FolderInfo newParentFolder, int year)
{
foreach (FolderInfo folderInfo in folder.EnumerateFolders())
{
FolderInfo newFolder = newParentFolder.GetSubFolder(folderInfo.DisplayName) ??
newParentFolder.AddSubFolder(folderInfo.DisplayName);
if (folderInfo.HasSubFolders)
{
ProcessSubfolders(folderInfo, newFolder, year);
}
newFolder.AddMessages(folderInfo.EnumerateMapiMessages().Where(m => m.DeliveryTime.Year == year));
if (newFolder.ContentCount == 0 && !newFolder.HasSubFolders && newFolder.DisplayName != "Deleted Items")
newParentFolder.DeleteChildItem(newFolder.EntryId);
}
}
You can see that all of the PST manipulation is very intuitive. Everything I needed to know, I was able to quickly learn from the documentation and the sample applications. It feels as if the classes are a part of the .NET Framework. It is a very well written API.
You can download the complete source code for the project here.
Summary
If you are working on any projects involving email processing or access, Aspose.Email can definitely simplify the code required to get the job done. I will definitely keep these libraries in mind for future projects and you should too.
Happy coding!
Disclosure of Material Connection: I received one or more of the products or services mentioned above for free in the hope that I would mention it on my blog. Regardless, I only recommend products or services I use personally and believe my readers will enjoy. I am disclosing this in accordance with the Federal Trade Commission’s 16 CFR, Part 255: “Guides Concerning the Use of Endorsements and Testimonials in Advertising.”
 Learn to Program with Scratch: A Visual Introduction to Programming with Games, Art, Science, and Math: Majed Marji: 9781593275433: Books
Learn to Program with Scratch: A Visual Introduction to Programming with Games, Art, Science, and Math: Majed Marji: 9781593275433: Books
 Professional Visual Studio 2013 (Wrox Programmer to Programmer): Bruce Johnson: 9781118832042: Books
Professional Visual Studio 2013 (Wrox Programmer to Programmer): Bruce Johnson: 9781118832042: Books
